TSP: ENHANCING PRODUCTIVITY WITH LOWER CARBON FOOTPRINT
OCP NUTRICROPS
OCP Nutricrops provides farmers with a wide variety of high-quality, sustainably produced, and customized phosphate-based soil health and plant nutrition solutions and promotes the adoption of advanced agronomic practices through collaboration with agronomists and experts across the world.
OCP Nutricrops helps farmers access effective and sustainable products that are fine-tuned for the specific needs of their soils, whatever their crop choice and wherever they are in the world.
Through advanced soil mapping and the creation of customized products, OCP Nutricrops promotes optimal soil health and helps farmers maximize their productivity while protecting the environment and combating climate change.
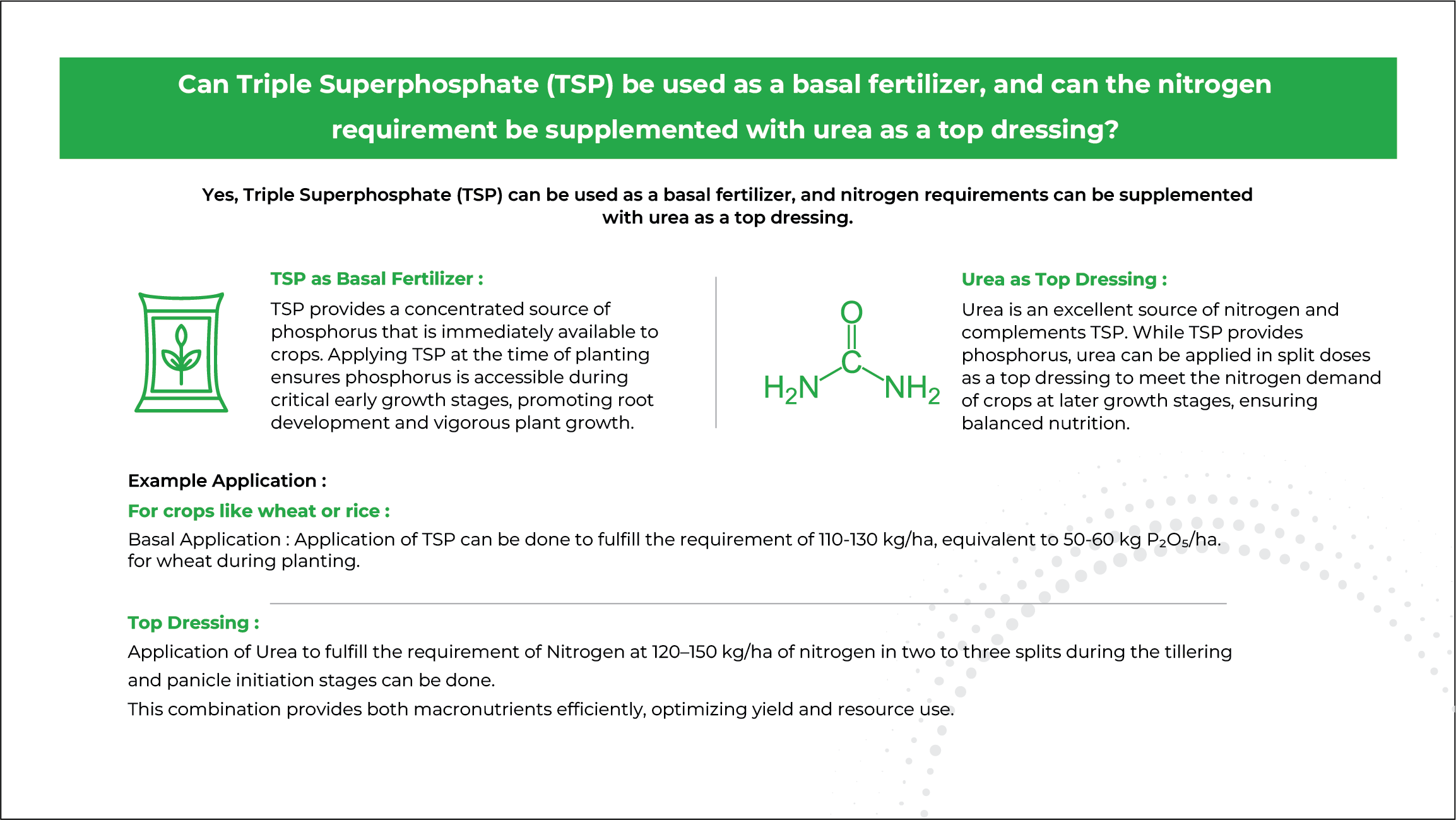
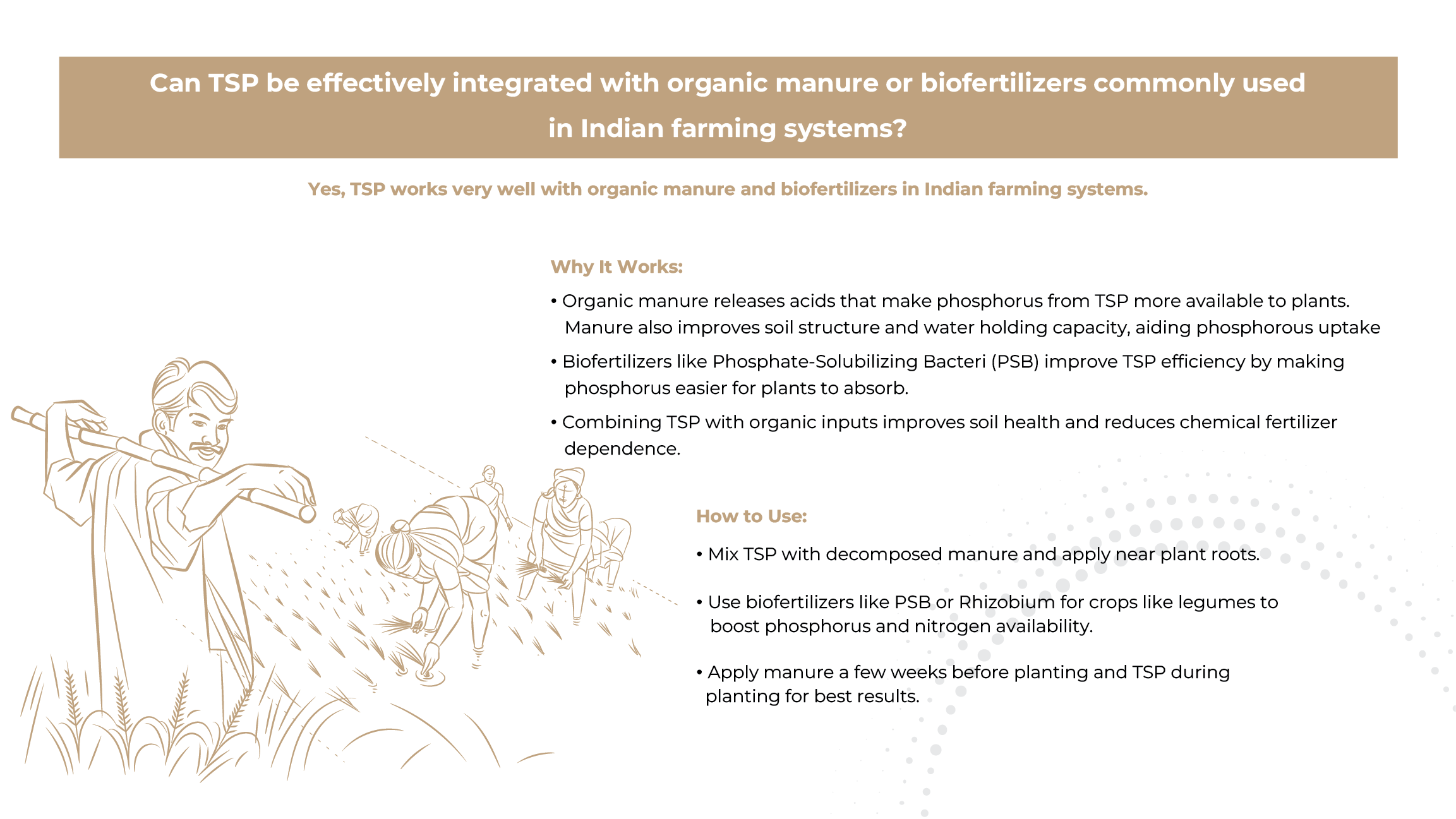
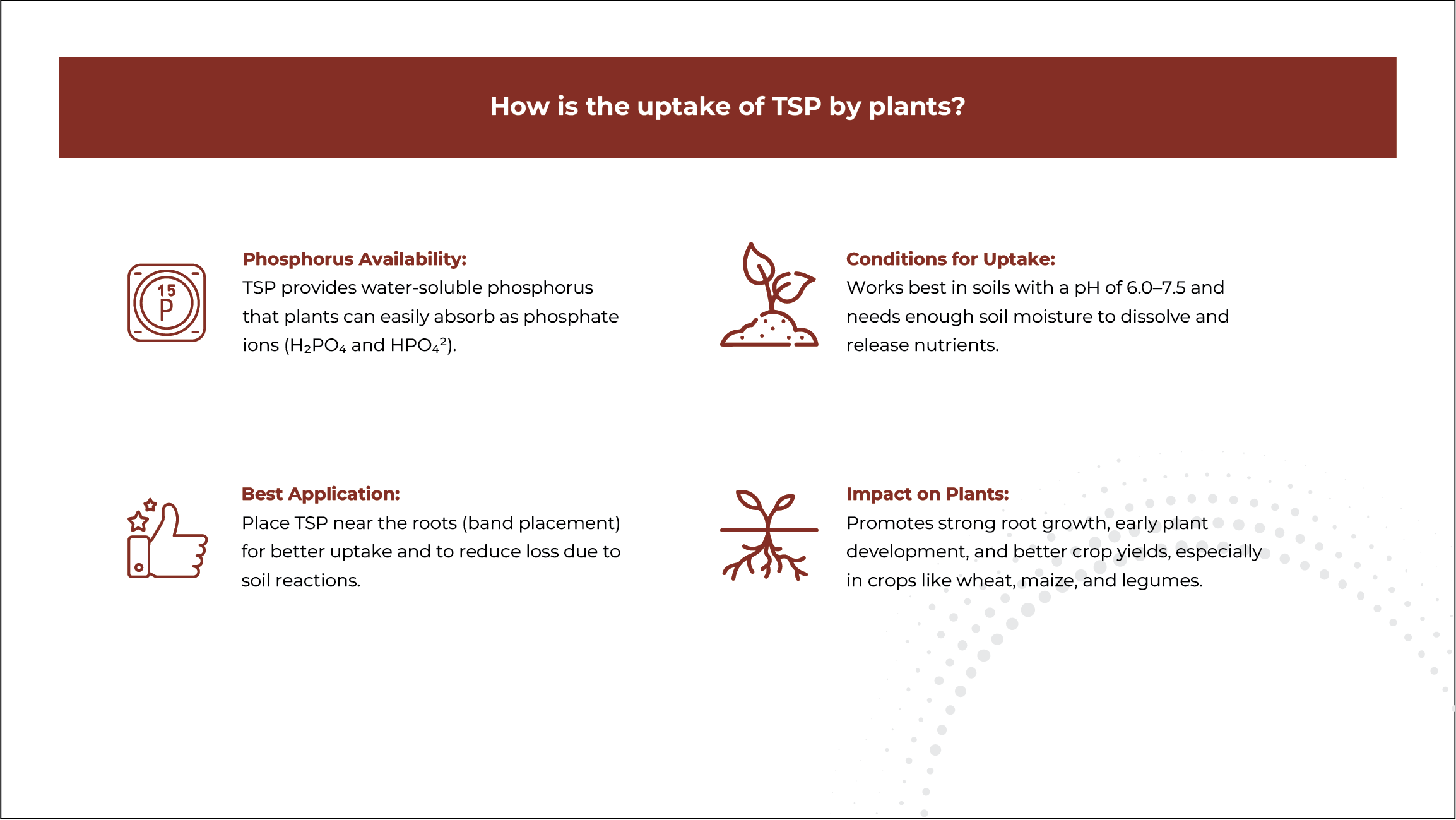
What is TSP?
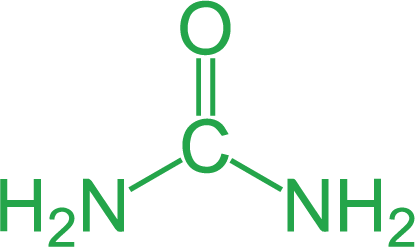
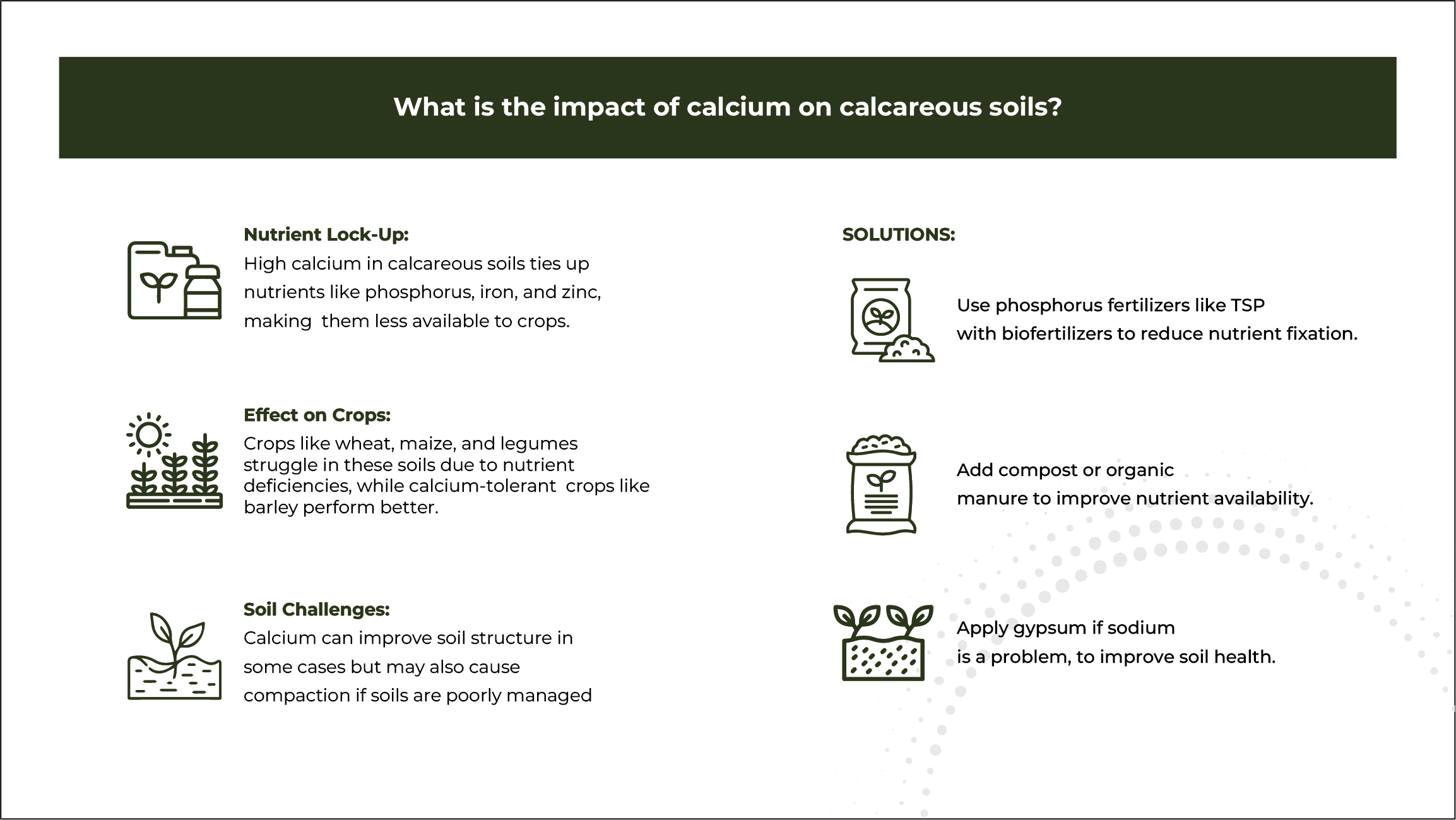
At least 90% of the total P within TSP is water soluble, so it becomes rapidly available for plant uptake. TSP has a granular form with equally sized grey color granules, making application through fertilizer spreading equipment very precise.

TSP
BENEFITS

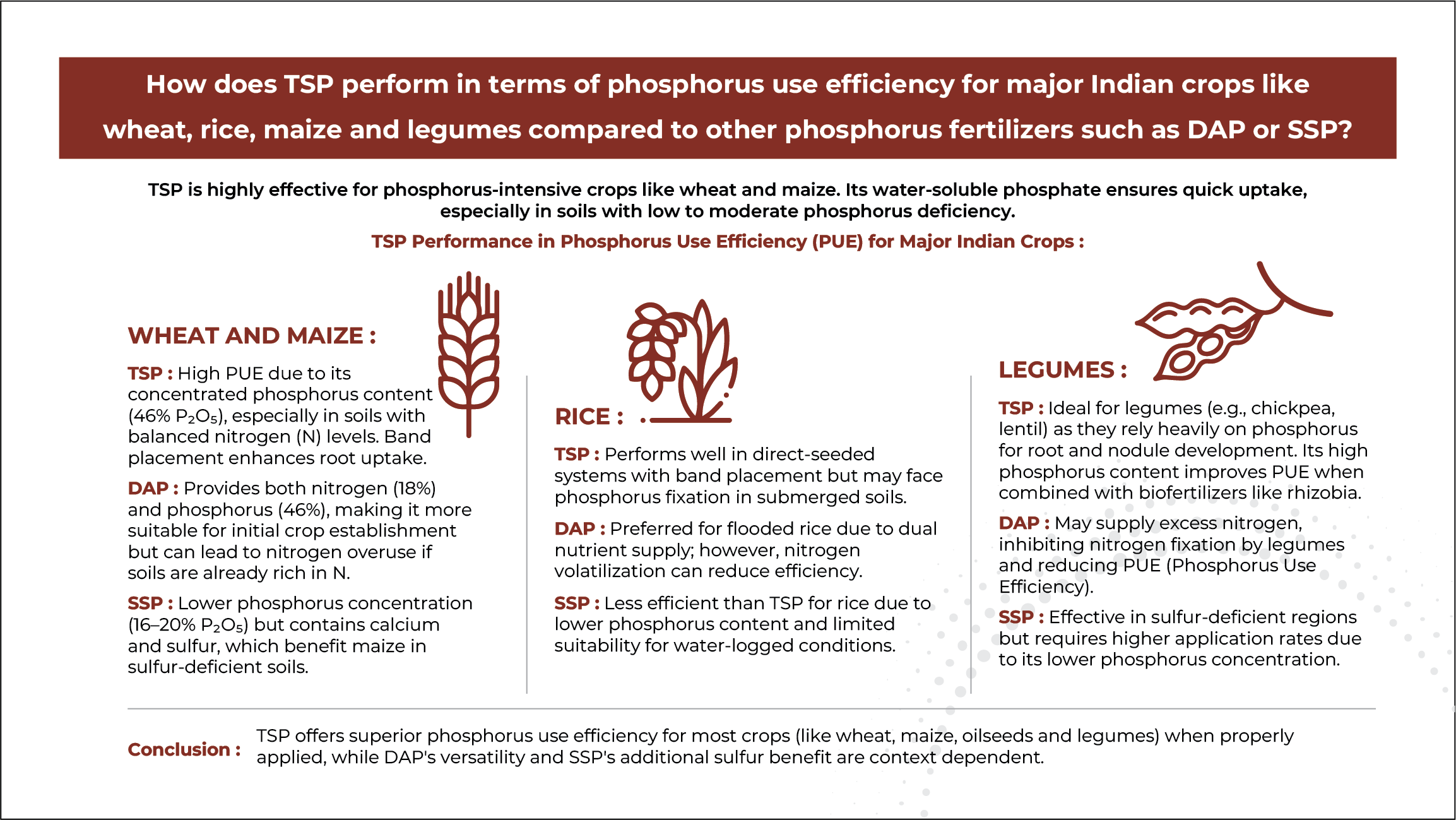
Ideal for a Wide Range of Crops:
Meets diverse
agricultural needs

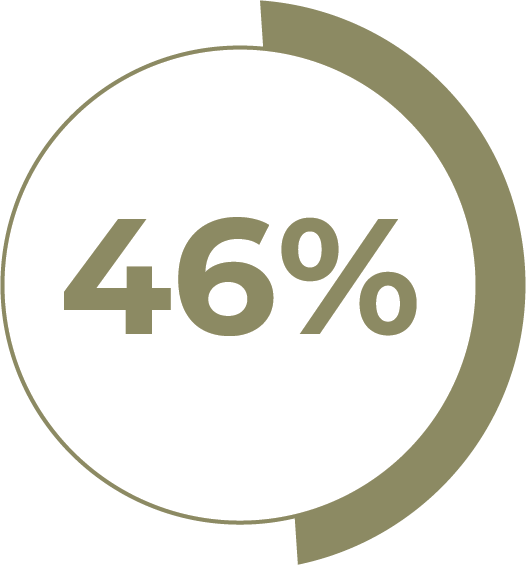
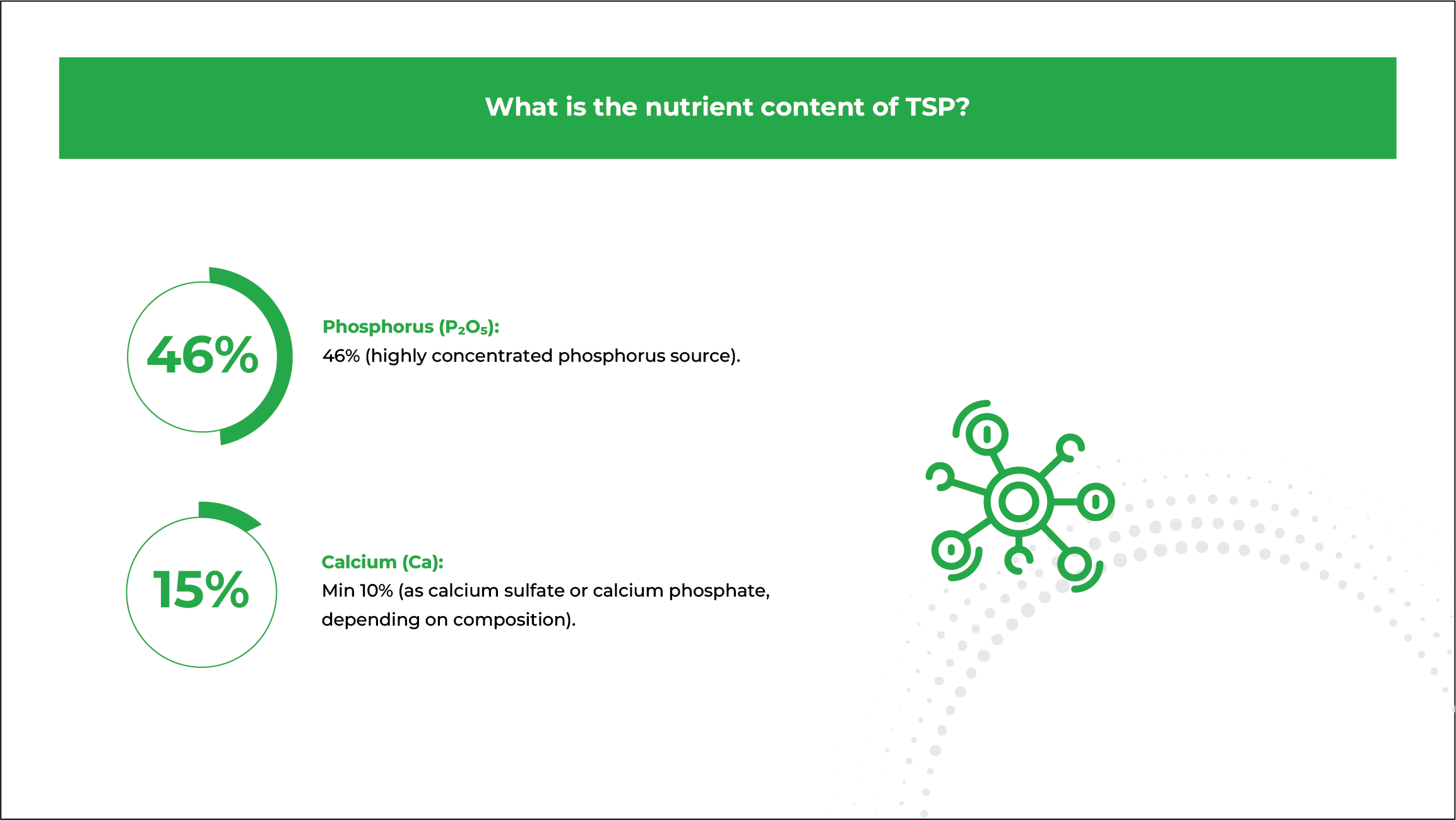
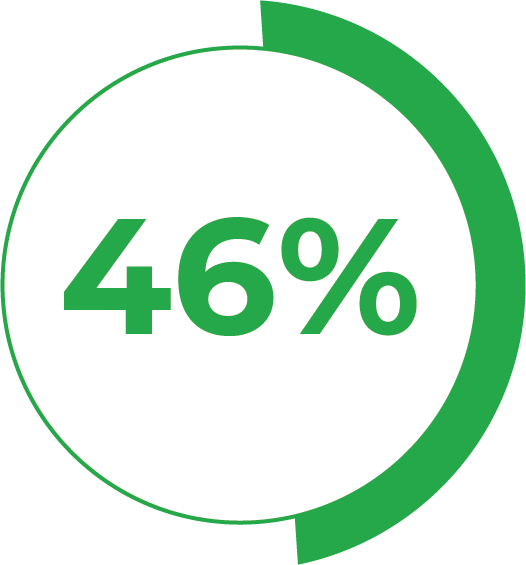
46% Phosphate:
Delivers essential
nutrients to the soil

+90% Water Solubility:
Ensures quick nutrient
absorption

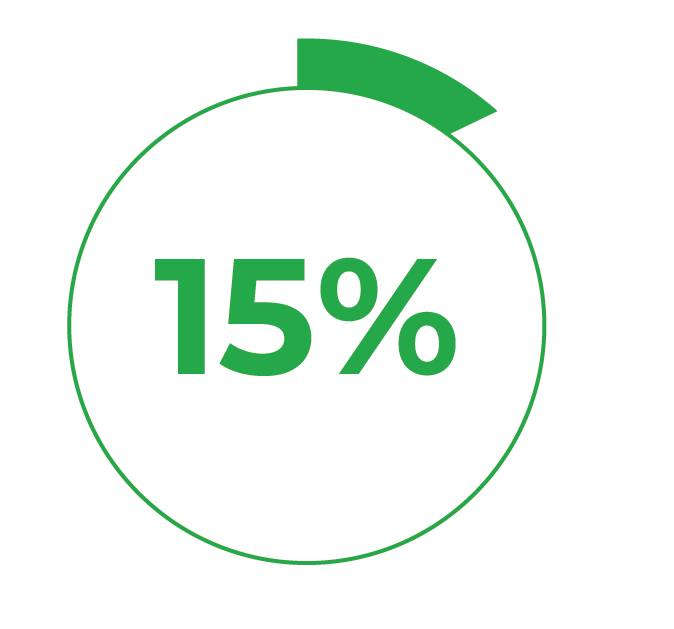
15% Calcium:
Supports balanced growth,
nutrition, and soil structure

Crop Development:
Promotes stronger
growth and higher yields

Ideal for a Wide Range of Crops:
Meets diverse
agricultural needs

+90% Water Solubility:
Ensures quick nutrient
absorption

15% Calcium:
Supports balanced growth,
nutrition, and soil structure

Crop Development:
Promotes stronger
growth and higher yields

46% Phosphate:
Delivers essential
nutrients to the soil





CROP FOCUSED SOLUTIONS
Pulses

RED, BLACK & GREEN GRAMS

LENTILS

PIGEON PEAS

CHICKPEAS
CROP FOCUSED SOLUTIONS
Cereals

WHEAT

RICE

MAIZE
CROP FOCUSED SOLUTIONS
Oilseeds
(Soybean , grondnut and Mustard)

SOY BEANS

GROUNDNUT

MUSTARD
CROP FOCUSED SOLUTIONS
Other crops
Sugarcane: TSP promotes strong roots, early tillering, and nutrient uptake. It boosts sugar accumulation, disease resistance, and overall plant vigor for higher yields.
Potato: TSP aids root development and tuber formation. It enhances starch accumulation, nutrient absorption, and yield quality.

COTTON
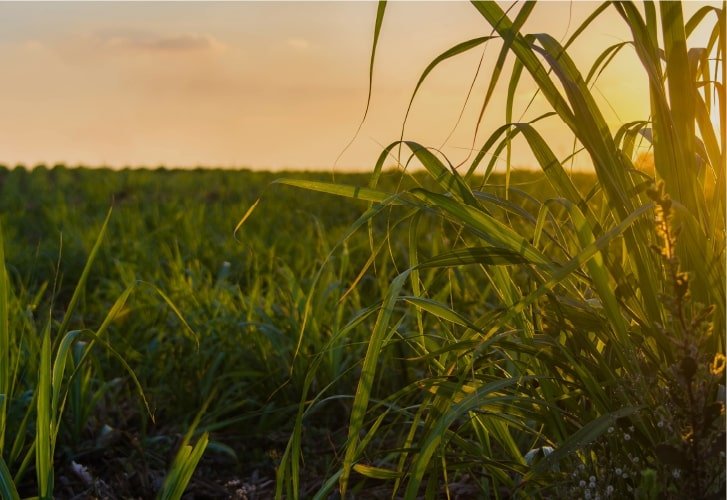

SUGARCANE
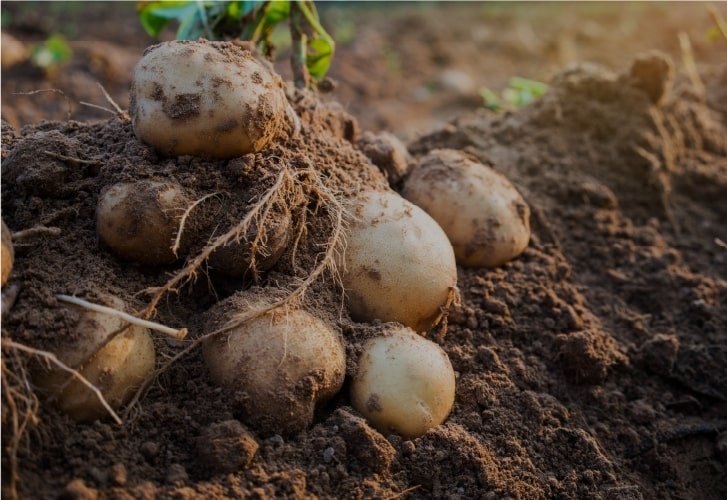

POTATO
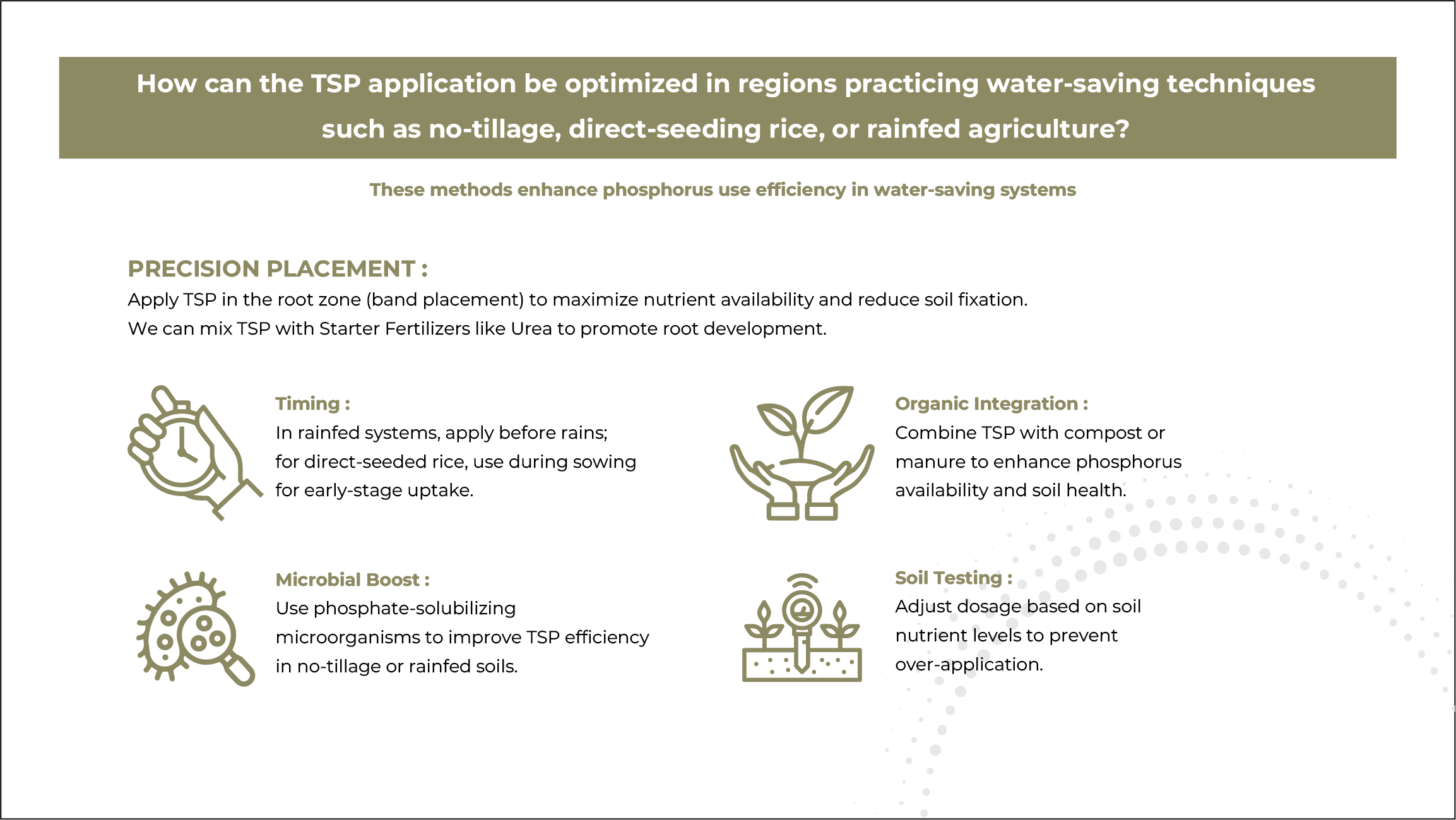
4R NUTRIENT STEWARDSHIP

Right Source
Matches fertilizer type to crop needs.

Right Time
Makes nutrients available when crops needs them.

4Rs

Right Rate
Matches amount of fertilizer type crop needs.

Right Place
Keep nutrients where crops can use them.
DO YOU WANT TO KNOW MORE?
TESTIMONIALS
Lakhwinder Singh
Crop: Potato
Aasish Kumar
Crop: Wheat & Mustard
Akhilesh Kumar Verma
Crop: Wheat